Google Docs
This page provides information on how to connect to Google Docs. It enables users to perform actions such as fetching documents and updating their content.
Connect Google Docs
To connect to Google Docs, authenticate using OAuth 2.0. This allows you to securely retrieve, create, and update documents through the integration. During authentication, you are prompted through a UI to authorize access to Google Drive and Google Docs.
During the authentication process, you must select both permission checkboxes in the authorization UI—one granting access to all Google Drive files, and the other granting access to specific files. Both permissions are required to ensure consistent access to newly created as well as existing documents.
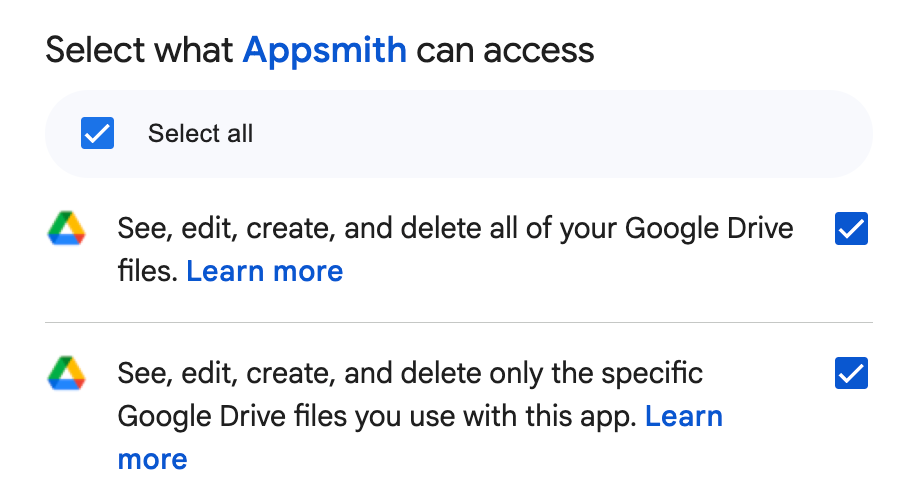
In addition, you must have view or edit access to any document you intend to fetch or update. Without the appropriate permissions on the file, requests will fail.
Query Google Docs
The following section is a reference guide that provides a description of the available commands with their parameters to create Google Docs queries.
Fetch Google Docs Content
Fetches the structured content of a specified Google Document using the Google Docs Integration. The output includes metadata and a full content tree composed of sections, paragraphs, text elements, styles, and optional links.
Google Document ID string
This property identifies the Google Document to retrieve. The ID is a unique string found in the document URL.
To locate it:
- Open your Google Document.
- Copy the portion of the URL between
/d/and/edit.
For example:
https://docs.google.com/document/d/19wEfeMnroEjjGyA_Uqxvvdi69QYlkEwPuY/edit
The Document ID is:
19wEfeMnroEjjGyA_Uqxvvdi69QYlkEwPuY
The document does not need to be public, but the connected Google account must have view or edit access.
The command returns a structured output object representing the document's contents, in line with the Google Docs API response schema.
Key properties include:
title: The title of the document.body.content[]: An array of structural elements including paragraphs, headings, and breaks.
Each item in the content array contains:
startIndex/endIndex: Position of the element in the document.paragraph: When present, contains a paragraphStyle, and elements[] with nested textRun objects.
Update Google Docs Content
Updates the content of a specified Google Document using structured requests defined by the Google Docs batchUpdate API.
Google Document ID string
The unique identifier of the document to update. This ID is found in the document’s URL and is required to target the correct file. The connected Google account must have edit access to apply changes.
Requests JSON array
This property accepts a JSON array of request objects that follow the Google Docs batchUpdate specification. Each object in the array defines a discrete document operation such as:
insertText: Add text at a specific index.deleteContentRange: Remove content between two indexes.updateTextStyle: Modify the styling of a specified text range.updateParagraphStyle: Change paragraph-level formatting.
Each object in the array follows this structure:
{
"insertText": {
"location": {
"index": 1
},
"text": "Your text here"
}
}
Understanding Document Indexing
Google Docs uses zero-based character indexing for all content positions in a document. Each character, including line breaks (\n), is counted in the index.
-
index:
1represents the position immediately after the start of the document. -
If you insert text at index
1, it will appear at the very top of the document body. -
To insert in the middle or at the end, you must provide a valid index derived from the document's structure.
Examples:
- Insert a Heading at the Start of the Document
[
{
"insertText": {
"location": { "index": 1 },
"text": "## Introduction\n"
}
}
]
- Delete a Block of Text (from index
50to100)
[
{
"deleteContentRange": {
"range": {
"startIndex": 50,
"endIndex": 100
}
}
}
]
- Update Content (Insert + Delete)
[
{
"deleteContentRange": {
"range": {
"startIndex": 20,
"endIndex": 30
}
}
},
{
"insertText": {
"location": { "index": 20 },
"text": "Revised text"
}
}
]
Tips:
- When submitting multiple operations in a single update request, always order them by descending index values. This prevents earlier changes (e.g., inserted text) from shifting the positions of later operations.
- Use the Fetch command to inspect current content and calculate index ranges.
- Chained operations should account for index shifts — inserting text at index 1 will push all later indexes forward.
- Use the appropriate request type depending on whether you're modifying structure (
insertText) or style (updateTextStyle).
Search Google Docs
Searches for Google Docs files that match the provided name using the Drive API.
Document Name string
The name or partial name of the document you are looking for. The search is case-insensitive and will return all matching Google Docs files the authenticated user has access to.
Example:
To find all documents with "Meeting Notes" in the name:
{{ searchInput.text }}
Create Google Docs File
Creates a new blank Google Document in the user's Google Drive.
Document Name string
The name to assign to the new document. This will appear as the document's title both in the Google Docs editor and in Drive. The name must be provided; otherwise, the creation will fail.
Example:
{{ newDocInput.text }}
Custom Action
Performs a fully customizable API call to the Google Docs or Google Drive endpoints. This command is designed for advanced use cases not covered by prebuilt actions, such as retrieving metadata, exporting documents, or interacting with Drive-level features.
Example 1: Retrieve Document Metadata
Fetches metadata for a specific document, such as name, MIME type, last modified time, and more.
Endpoint
GET https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files/<document_id>
Request
- Base URL:
https://www.googleapis.com - Path:
/drive/v3/files/<document_id> - Method:
GET
Query Params
fields: Optional. To limit the response, you can specify fields such as name,mimeType,modifiedTime.
https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files/1Zu34TY5215td1NxQliZkqFjhX5s?fields=name,mimeType,modifiedTime
Example 2: Export Document as PDF
Exports a Google Document as a PDF file.
Endpoint
GET https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files/<document_id>/export?mimeType=application/pdf
Request
- Base URL:
https://www.googleapis.com - Path:
/drive/v3/files/<document_id>/export - Method:
GET
Query Params
mimeType=application/pdf
https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/files/1Zu34TY5dR5td1NxQliZkqFjhX5s/export?mimeType=application/pdf