Git Settings
This page provides information on all Git-related settings available within Appsmith. These properties become available once you've connected your app to Git. You can access these settings by clicking on the gear icon located on the bottom bar.
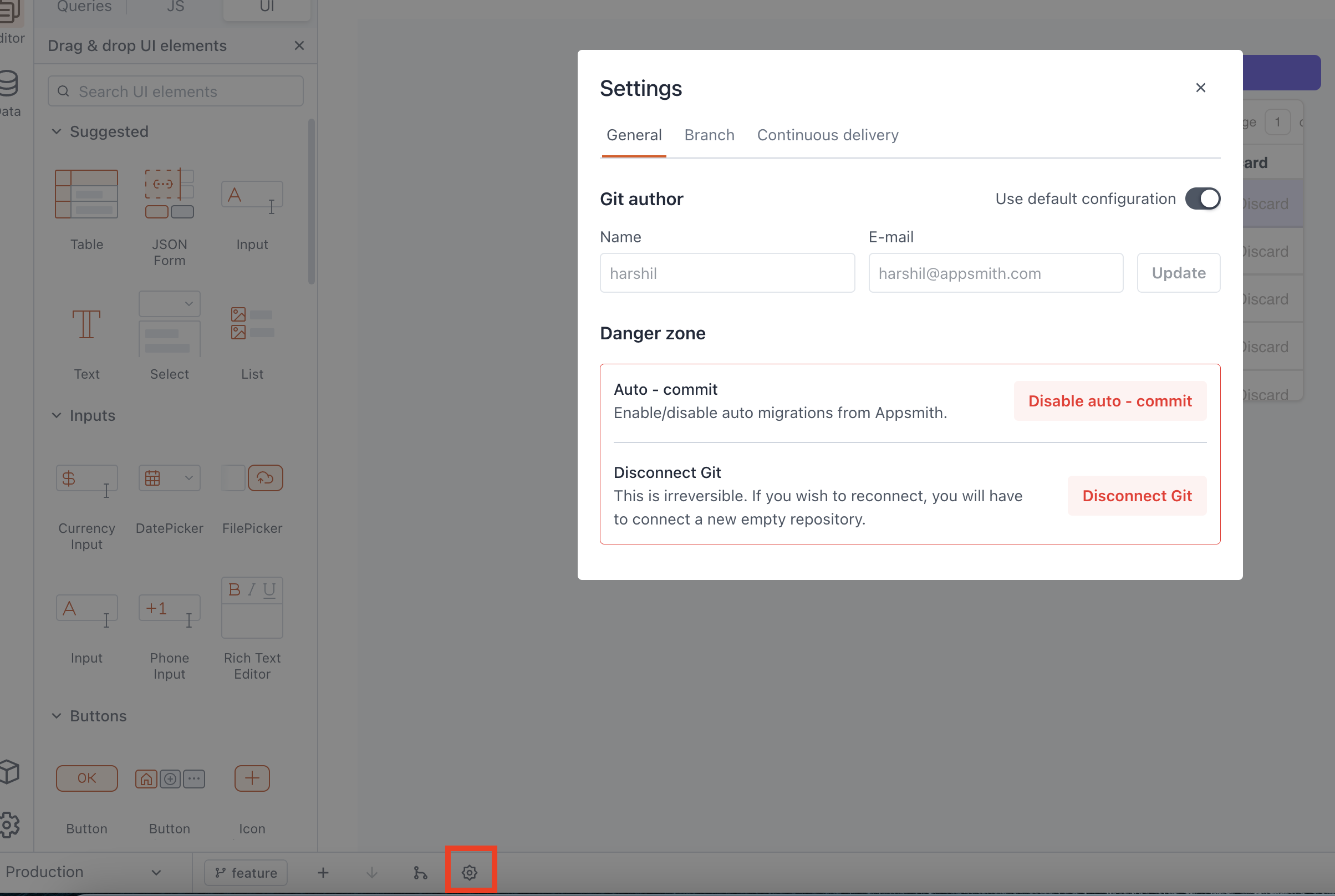
General
These properties are customizable options accessible within the Git settings modal.
Git author
This section allows you to modify the name and email associated with the author. You can choose to either use the default settings or disable the Use Default Configuration button and add a new name and email.
- Name: You can update the Git author's name, which changes how your identity is displayed in the commit history.
- Email: You can specify a new email address. This change affects how your contributions are linked and identified across the repository's history.
Danger zone
This section allows you to change important Git settings such as disabling auto-commit or disconnecting Git from Appsmith.
Disable Auto-Commit:
The Auto Commit feature in Appsmith automatically commits changes related to version upgrades. When auto-commit is enabled, it:
-
Automatically commits changes to a non-protected branch when you open the branch in your app. If the app is not actively in use, the auto-commit will not take place.
-
Commits only the changes related to Appsmith's Domain Specific Language (DSL) components, not your specific app changes.
If you disable auto-commit, it prevents automatic changes from Appsmith, potentially resulting in uncommitted system changes after an Appsmith instance upgrade. This may require manual handling and could lead to discrepancies in Git versioning.
Example:
When Appsmith updates its version and auto-commits changes, only updates related to the Table widget—such as new properties or methods—are committed. Your customizations, like styling or data updates, remain unaffected. DSL-related changes can be found in your Git repository within the relevant page folder.
//example dsl code
"dsl": {
"widgetName": "MainContainer",
"parentRowSpace": 1,
"type": "CANVAS_WIDGET",
"canExtend": true,
"version": 89,
"minHeight": 1292,
"parentColumnSpace": 1,
},
Disconnect Git:
This action permanently disconnects your Appsmith app from Git. Once disconnected, it is not possible to reconnect to the same repository. If you want to reconnect, you need to connect a new empty repository.
Branch
These settings are customizable options available for modifying branch-related settings.
Default branch
This property allows you to modify the default branch, which determines the base branch of your app. If there is no branch tag in the App URL, users are directed to the app associated with this branch.
You can choose a different default branch for each instance, while the default branch on Git remains unchanged until modified in the Git provider settings.
Example: You can set the master branch as default for the production instance and the staging branch as default for the staging instance. Meanwhile, the default branch on Git remains unchanged, usually set as master by default.
Branch protection
This property allows you to set multiple branches as protected, meaning that changes to the app are not allowed within those branches. To make changes to these branches, you need to raise a PR and merge it manually from the Git provider.
Continuous delivery
The CI/CD feature in Appsmith enables you to automatically deploy changes to the selected branch, eliminating the need to manually pull updates after each change.
-
CURL command: The provided CURL command is specifically intended for configuring automatic deployments within Appsmith's CI/CD setup. It triggers a POST request to the specified endpoint, initiating the deployment process for the designated app and branch.
-
Bearer token: You can use this bearer token for authenticating CI/CD requests. You can add this bearer token to your secrets or environment variables for secure access. Once generated, paste your bearer token immediately. You won't be able to do this later.
For more information see Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) with Git