GIT Apps with Packages Best Practices
This page provides essential best practices for working with Git-connected applications that use Packages, helping you maintain synchronization between your applications and their dependencies, and ensuring smooth deployments across different workspaces and instances.
Non Git-Connected Packages
When working with a Git-connected application that uses non Git-connected Packages, you need to ensure that Package updates are properly synchronized to the deployed version of your application.
Synchronizing Package Updates
Whenever a non Git-connected Package is updated, follow these steps to ensure the latest changes are reflected in the view mode of your Git-connected application:
-
Navigate to the Git-connected application in edit mode.
-
Open the Git commit modal by clicking the Commit icon button in the bottom bar or the Deploy button on the top right of the editor.
-
Click Redeploy from the Git modal to synchronize the latest Package changes to view mode.
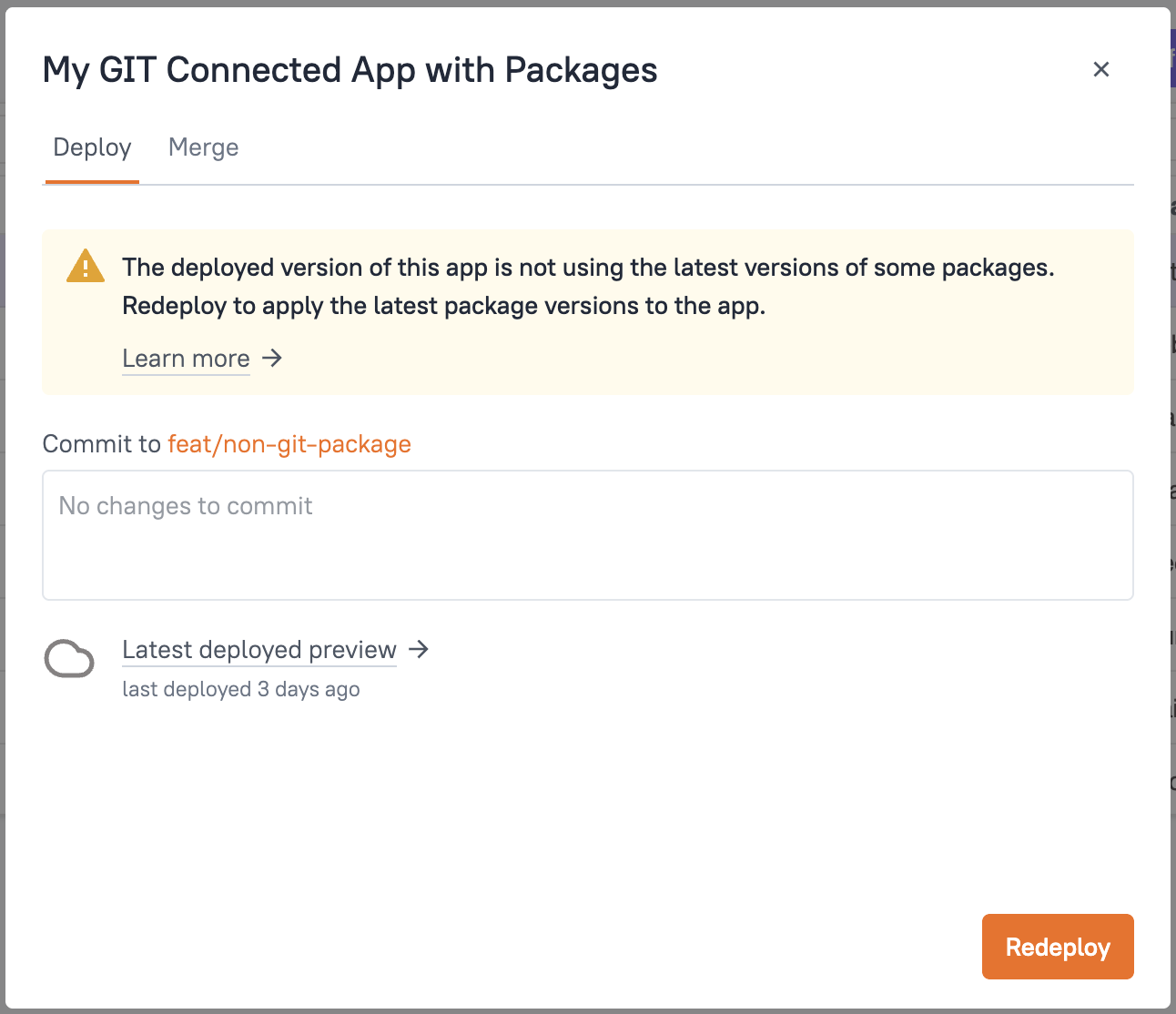
Alternatively, if there are any pending commits to be made to the application itself, making a commit will also ensure that the latest Package-related changes are deployed to view mode. The commit process automatically includes Package updates in the deployment.
Git-Connected Packages
When working with a Git-connected application that uses Git-connected Packages, you need to manually update the Package version in your application after a new version is published and released.
Updating Package Versions
When a Git-connected Package is published and released with a new version, follow these steps to update your application to use the new version:
-
Navigate to the Git-connected application in edit mode.
-
Open the Libraries section from the sidebar.
-
Under Packages, locate the Package that was updated and switch the version to the new one that was published.
-
Commit the changes to the application to synchronize the Package changes to view mode.
If you don't redeploy or commit after updating a Package, the changes will only be visible in edit mode. The deployed (view mode) version of your application will continue to use the previous Package version until you redeploy or commit.
Importing Git-Connected Apps with Packages
When moving a Git-connected application that uses Packages to a new workspace or instance, it's important to follow the correct sequence to ensure the application can properly detect and use its Package dependencies.
Migration Steps
Follow these steps in order when importing a Git-connected application that uses Packages:
-
Move Packages first: Import or create the Packages that the application uses in the target workspace or instance. If you're moving to a different instance, you may need to export and import Packages, or recreate them in the new instance. Ensure all Package dependencies are available before importing the application.
-
Publish Packages: Publish the Packages in the new workspace or instance to make them available. For non Git-connected Packages, a publish is required to make them available in the new workspace or instance. For Git-connected Packages, they are already published and released as a particular version, so publish is not required.
-
Import the Git-connected application: After the Packages are set up and published, import the Git-connected application. The application will immediately detect the available Packages based on their names and structure. Ensure that Package names match exactly between the source and target workspaces or instances for proper detection.
-
If the application was imported first: If you import the Git-connected application before setting up the required Packages, the application will not detect the Packages and may throw errors. To resolve this, import the packages in the workspace or instance, publish them if they are non Git-connected Packages, then navigate to the application in edit mode, open the Git modal, and click Redeploy to synchronize the Package changes to the application's view mode.
CI/CD with Git-Connected Apps and Packages
When using Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) with Git-connected applications that use Packages, there are different considerations depending on whether the Packages are Git-connected or not.
Non Git-Connected Packages
For non Git-connected Packages, CI/CD will not automatically handle Package updates. You still need to follow the manual steps mentioned in Synchronizing Package Updates to update the Packages and applications using them.
Git-Connected Packages
For Git-connected Packages, CI/CD will continue to work as expected, but you need to ensure that the Package already exists in the application's workspace. Follow the steps mentioned in Migration Steps to set up the Package in the workspace before the CI/CD process runs.
Prerequisites for CI/CD
In both scenarios, the expectation is to:
- Import the packages if it is not already present in the application's workspace.
- Merge the commits to the
masterbranch of the application to initiate the CI/CD process.
Resolving CI/CD Failures
If CI/CD fails because a new Package is not present in the workspace, follow these steps to resolve it:
- Import the Package in the application's workspace.
- If it is a non Git-connected Package, publish it to make it available.
- Then redeploy the application by either of the below steps:
- Rerun the failed CI/CD workflow to automatically deploy the application with the newly imported Package.
- Navigate to the application in edit mode, open the Git modal, and click Redeploy to synchronize the changes to the view mode.